How to Treat and Prevent Age Spots
Age spots are one of the most common skin concerns among adults over 40. These flat, darkened areas on the skin often appear on the face, hands, shoulders, and arms, which are the parts of the body most exposed to the sun. While they are generally harmless, many people want to reduce or prevent them for cosmetic reasons.
At Benson Dermatology, we help patients understand what causes age spots, how to treat them, and how to keep their skin looking youthful for as long as possible. Today, our board-certified dermatologists explore what age spots are, why they form, how to treat them effectively, and what steps you can take to help prevent them from developing in the first place.
What Are Age Spots?
Age spots, also called liver spots or solar lentigines, are small, darkened patches of skin. They range in color from light brown to black and typically vary in size from a freckle to a half-inch in diameter. While they are often associated with aging, age spots are actually caused by prolonged sun exposure over time. The name “age spots” comes from their tendency to appear in later life, usually after the age of 40, although they can develop earlier.
These spots are usually flat and painless. Unlike freckles, which can fade with reduced sun exposure, age spots tend to persist once they appear. They are most commonly seen in people with fair skin but can develop in anyone regardless of skin tone.

What Causes Age Spots
The primary cause of age spots is repeated exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun or tanning beds. UV light accelerates the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for giving skin its color. Over time, UV exposure can trigger melanin to clump together or be produced in higher concentrations, creating dark patches in the skin.
In addition to UV exposure, other risk factors include:
Age: The older you are, the more sun exposure you've had. That cumulative damage increases your risk.
Genetics: Some people are simply more prone to developing age spots based on family history.
Skin Type: People with lighter skin are more likely to develop age spots due to less natural protection from UV rays.
Tanning Beds: Artificial UV light can have the same impact as natural sunlight and increase age spot development.
Are Age Spots Dangerous?
In most cases, age spots are harmless and do not require medical treatment. However, any new or changing spot on your skin should be examined by a dermatologist to rule out skin cancer. Melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, can sometimes mimic the appearance of a benign age spot.
You should schedule an evaluation if a spot:
- Changes in size, shape, or color
- Has an irregular border
- Becomes painful, itchy, or starts to bleed
- Has a mix of colors
At Benson Dermatology, our team can quickly determine whether a skin lesion is benign or requires further testing.
How to Treat Age Spots
There are several ways to treat age spots, ranging from over-the-counter products to professional dermatological procedures. The best approach depends on the size, location, depth, and darkness of the spots, as well as your skin type and goals.
Dermatologists often prescribe creams containing hydroquinone, tretinoin, or corticosteroids. These ingredients work to gradually fade age spots by slowing melanin production and increasing skin cell turnover. Results may take several weeks to months, but these creams are generally effective for mild to moderate age spots.
Many OTC products contain ingredients like niacinamide, vitamin C, glycolic acid, kojic acid, or licorice root extract. While not as strong as prescription creams, they can help brighten skin and lighten pigmentation over time when used consistently.
Retinoids derived from vitamin A can also promote cell turnover and reduce the appearance of pigmentation. Retinol, available in OTC products, is less potent than tretinoin but can still produce noticeable results with regular use.
Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin to exfoliate the top layers and promote new cell growth. This process can lighten age spots and improve overall skin tone. Peels vary in strength, from light glycolic acid peels to deeper trichloroacetic acid (TCA) options.
Peels may cause temporary redness, flaking, or sensitivity, but they are often effective for treating surface-level pigmentation. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
Cryotherapy, or freezing, involves applying liquid nitrogen to the age spot to destroy excess pigment. This method is often used for single, well-defined spots. After the treatment, the area may blister and then scab over before healing.
Cryotherapy is quick and relatively inexpensive, though it carries a small risk of skin lightening or scarring in some individuals.
Laser therapy targets melanin with concentrated light energy, breaking up pigment clusters in the skin. This method is highly effective for deeper or more stubborn age spots. Common types of lasers used include:
- Q-switched lasers
- Fractional lasers
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
Laser treatments usually require a series of sessions. Some patients may experience temporary redness or swelling. The benefit of laser therapy is precise targeting with minimal damage to surrounding tissue.
Microdermabrasion uses a device to exfoliate the outer layer of the skin, helping to fade superficial pigmentation. This method is less aggressive than chemical peels or lasers but can improve skin texture and tone with repeated treatments.
It is ideal for those looking for a gentle, gradual improvement in skin appearance without downtime.
Microneedling creates tiny punctures in the skin to stimulate collagen production and encourage cell renewal. It can be combined with serums or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to enhance results. While it is more commonly used for acne scars and wrinkles, microneedling can help fade pigmentation when done in a series.
Prevention
How to Stop Age Spots Before They Start
Preventing age spots comes down to protecting your skin from sun damage. While you can't undo past exposure, you can take steps starting today to minimize future pigmentation.
Wearing sunscreen every day is the most important thing you can do to prevent age spots. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, and apply it to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days or in winter. Reapply every two hours if you're outside, and more often if you're sweating or swimming.
Covering your skin can block UV rays. Consider wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves when spending time outdoors. UV-protective clothing is also available and especially helpful for people with sun-sensitive skin.
Try to stay in the shade between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the sun’s rays are strongest. If you're out during this time, seek shade or use an umbrella.
Tanning beds expose your skin to concentrated UV radiation, increasing your risk of age spots, wrinkles, and skin cancer. There is no safe way to tan using artificial UV light.
Antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, green tea extract, and niacinamide can help protect your skin from free radicals and oxidative stress caused by sun exposure. Many serums and moisturizers now include these ingredients to provide an extra layer of defense.
While hydration and nutrition do not directly prevent age spots, they support overall skin health. Eating foods rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and vitamins can improve your skin's ability to recover from damage and reduce inflammation.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice dark spots on your skin and are unsure what they are, it's important to consult with a dermatologist. While most age spots are harmless, a professional can distinguish between benign pigmentation and signs of skin cancer.
You should also seek treatment if:
- The spots are getting darker or growing quickly
- You want faster or more noticeable cosmetic improvement
- Over-the-counter products have not helped
- You are unsure what kind of skin condition you are dealing with
At Benson Dermatology, we provide accurate skin evaluations and can tailor a treatment plan based on your goals, skin type, and medical history.
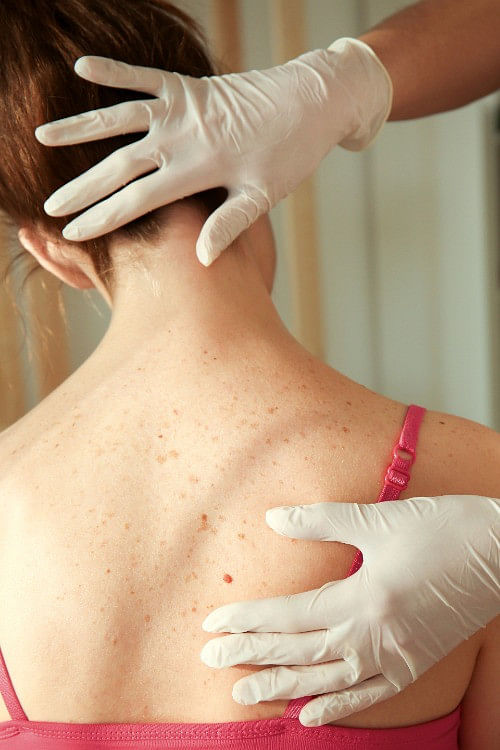
Choosing the Right Treatment for You
Not every treatment works the same for everyone. Some people may respond well to topical treatments, while others need in-office procedures for more significant results. Your skin tone, budget, and tolerance for downtime all play a role in deciding which approach is best.
Our team at Benson Dermatology can walk you through your options and explain the pros and cons of each method. Often, a combination of treatments and preventive skincare works best to maintain a more even, youthful appearance over time.
Spot the Spot with Benson Dermatology
Age spots are a natural result of sun exposure over time, but they don't have to be permanent. With the right knowledge, preventive habits, and access to expert care, you can reduce their appearance and keep new ones from forming. Whether you choose a prescription cream, laser therapy, or a professional skincare routine, there are more options than ever to help your skin look its best.
If you're ready to treat age spots or want to learn how to prevent them, contact Benson Dermatology today. Our board-certified dermatologists are here to help you achieve clear, healthy, and radiant skin with personalized care every step of the way.


